What Is ABS Or Anti-Lock Braking System, EBA, ESP, TCS
Hello guys, welcome back to our blog. In this article, we will discuss what is ABS or anti-lock braking system, the working of ABS, EBA (Emergency Brake Assist), ESP (Electronic Stability Program), and TCS (Traction Control System).
If you have any electrical, electronics, and computer science doubts, then ask questions. You can also catch me on Instagram – CS Electrical & Electronics.
Also, read:
- Why Working From Home Is Better Than Going To Office Must Know
- Top 20 AUTOSAR Interview Questions For AUTOSAR Engineers
- Products Manufactured By Texas Instruments In Various Domains
Anti-Lock Braking System, EBA, ESP, TCS
Nowadays safety is important in vehicles because vehicles are used by many people to go from one place to another place, but the thing is safety which people want while driving a car or riding a bike. In earlier days, when the driver pressed the brake suddenly then an accident was taking place because of a lack of control of the car or bike.
But at present due to technology like ABS, EBA, ESP, and TCS the accident rate has reduced. Each and every new vehicle has ABS (Anti-lock braking system) in it which will reduce road accidents. Now, we will discuss one by one ABS, EBA, ESP, and TCS.
ABS Or Anti-Lock Braking System
ABS or Anti-lock Braking System is a safety thing or system for the vehicle and also for the driver. The ABS is also called an anti-skid braking system. The ABS comes into action when the driver suddenly presses the brakes during an emergency condition. Nowadays, all company vehicles are employing the ABS system in the world. Whenever the driver suddenly presses or applies the brakes at a high-speed vehicle, there is always a chance of the wheel locking.
It provides the controlling actions that are designed to allow safe braking in emergency stops. Generally, during Hard-braking conditions, the wheels of the vehicle tend to lock. The rotation of the wheels stops and the wheel loses grip with the road and enters a skid. It is not possible to control the direction of the vehicle since the wheels are locked.
The ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) provides a breakthrough for unsafe braking conditions and enhances passenger safety. An ABS consists of,
- Brake Pedal
- Brake Pressure Modulator
- Brake Fluid Reservoir
- ABS Controller
- Wheel Speed Sensor
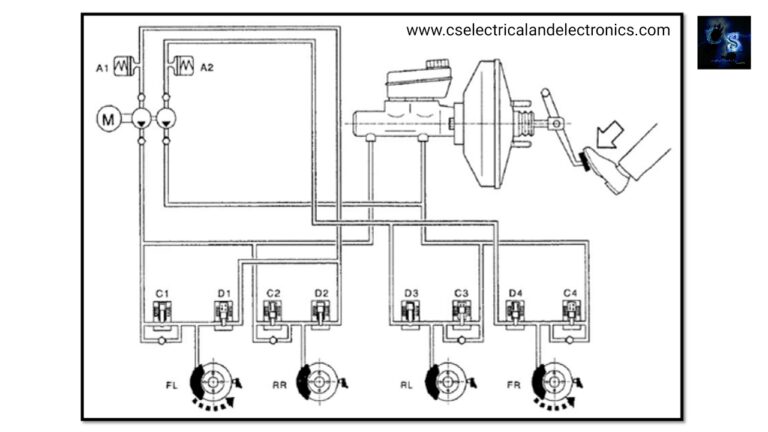
The wheel speed sensor continuously estimates the speed of each wheel of the vehicle. While the vehicle is moving at normal speed the ABS will not get into action. When quickly the driver applies the brake due to an emergency and if the speed sensor detects that the speed of any of the wheels is decreasing drastically, then it indicates that the wheel is going to be locked.
The locked wheel makes the vehicle out of control like skidding start taking place. Due to skidding, an accident may take place, so to avoid this Anti-lock Braking System is employed.
The ABS controller senses a variation in vehicle speed and proportional wheel speed. The Anti-lock Braking System module orders the brake control unit to decrease the braking force of the locking wheel, decreasing the braking force means decreasing the hydraulic pressure in the brake line running on the wheel. The brake control unit decreases the line pressure with the help of value in the system.
When the braking force decreases, the wheel begins rotating at a higher speed, thereby avoiding the wheel lock. As the wheel doesn’t lock, the steerability of the vehicle remains intact. That indicates that the vehicle runs according to the driver’s input without skidding. Once the normal state is returned, the brake control unit restores the hydraulic pressure with the help of a pump in the brake line.
While during abnormal conditions, the fluid pressure is raised again and the wheels are braked. This occurs at a rate of 10 times a second and stays until the vehicle stops.
TCS Or Traction Control System
The differential gear in the driving axles of a vehicle allows the wheel on the inside of a corner to rotate more slowly than the outside wheel of the corner. Yet, this same differential action can begin to lose traction (wheel spin).
If for any reason one driving wheel is on a smooth surface the wheel will spin and the wheel on the other side of the axle will be at standstill. As an outcome, the vehicle loses traction.
The TCS tries to return the traction. Traction control allows the brake to be applied to the wheel on a slippery surface. Hence more torque reaches the other wheel. This helps the vehicle to pass. TCS can be for front wheels or back wheels or every four wheels based on FWD or RWD or AWD.
ESP Or Electronic Stability Program
Electronic stability control (ESC), too called dynamic stability control (DSC) or electronic stability program (ESP), is an automated technology that enhances a vehicle’s stability by identifying and reducing the loss of traction (skidding). When ESC identifies a loss of steering control, it automatically implements the brakes to help “steer” the vehicle where the driver intends to go.
Braking is automatically achieved to wheels separately, so as the inner rear wheel counter understeer or the outer front wheel counter oversteer. Some ESC methods also minimize engine power until control is recovered.
During regular driving, ESC runs in the background and continuously observes steering and vehicle direction. It compares the driver’s required direction (estimated by the measured steering wheel angle) to the vehicle’s original direction (estimated by measured lateral acceleration, individual wheel speeds, and vehicle rotation (yaw)).
EBA Or Emergency Brake Assist
Brake Assist (BA or BAS) or Emergency brake assist (EBA) is a used automobile braking technology that increases the braking force in an emergency. A study conducted in 1992 at the Mercedes-Benz driving simulator in Berlin exposed that higher than 90% of drivers miss braking with enough force if met with an emergency.
Several drivers are not prepared for the highest efforts needed for maximum braking, nor are they prepared for the “buzzing” feedback in the brake pedal during the ABS operation. If an emergency happens, a slow reaction and less than maximum braking input could result in insufficient time or a way to stop before an accident happens.
EBA is meant to identify such “panic stops” and employ maximum braking effort in milliseconds. It interprets braking performance by assessing the rate at which the brake pedal is actuated. If the system recognizes an emergency, it automatically initiates full braking more speedily than any driver can move his or her foot. Emergency stopping lengths can be shortened, decreasing the likelihood of accidents – particularly the common “nose-to-dock” incident.
A system(Electronic) intended to classify emergency braking operations and automatically enhance braking force increases vehicle and occupant safety and can decrease stopping distances by up to 70 ft (21 m) at 125 mph (201 km/h).
I hope this article may help you all a lot. Thank you for reading. If you have any doubts related to the “ABS or Anti-lock Braking System, ESP Or Electronic Stability Program, TCS Or Traction Control System, EBA Or Emergency Brake Assist“, then comment below.
Also read:
- 100 + Electrical Engineering Projects For Students, Engineers
- 1000+ Electronics Projects For Engineers, Diploma, MTech Students
- 1000+ MATLAB Simulink Projects For MTech, Engineering Students
- 500+ Embedded System Projects For Engineer, Diploma, MTech, PhD
- 500+ Projects For Diploma Electrical, Electronics Student, Diploma Project
- 8051 Microcontroller Timers, TCON Register, TMOD Register
- Advancements In 3D Printing Technology And It’s Future
- Advancements In Power Electronics For Energy Efficiency
Author Profile
- Chetu
- Interest's ~ Engineering | Entrepreneurship | Politics | History | Travelling | Content Writing | Technology | Cooking
Latest entries
 All PostsApril 19, 2024What Is Vector CANoe Tool, Why It Is Used In The Automotive Industry
All PostsApril 19, 2024What Is Vector CANoe Tool, Why It Is Used In The Automotive Industry All PostsApril 13, 2024What Is TCM, Transmission Control Module, Working, Purpose,
All PostsApril 13, 2024What Is TCM, Transmission Control Module, Working, Purpose, All PostsApril 12, 2024Top 100 HiL hardware in loop Interview Questions With Answers For Engineers
All PostsApril 12, 2024Top 100 HiL hardware in loop Interview Questions With Answers For Engineers All PostsMarch 22, 2024Driver Monitoring Systems In Vehicles, Working, Driver Sleepy Alert
All PostsMarch 22, 2024Driver Monitoring Systems In Vehicles, Working, Driver Sleepy Alert