What is Distance Relay, Working, Advantages, Disadvantages, Applications
Hello guys, welcome back to my blog. In this article, I will discuss what is distance relay, the working of distance relay, its advantages, disadvantages, applications of it, types of distance relay, etc.
If you have any doubts related to electrical, electronics, and computer science, then ask questions. You can also catch me @ Instagram – Chetan Shidling.
Also, read:
- How High Voltage Electrical Gloves Work And Are Made Up Of
- Top 15 IoT Projects For Electrical Engineers, Electrical Engineering Project
- What Is Reactor, Types Of Reactors Used In Power Systems, Applications
Distance Relay
What is Distance Relay?
The impedance relay, distance protection element, or voltage-controlled device is another name for the distance relay. The distance between the impedances of the places where the fault occurs and where the relay is situated determines how well it works (feeding point). When the voltage and current ratio is changed to a specified value or less than the relay set value, the relay is activated. This type of relay is used to safeguard transmission and distribution lines from backup protection, fault protection, phase protection, and main protection.
The distance relay is a basic overcurrent relay with a simple design. Below is a schematic of a distance relay with voltage and current characteristics. The operating state at a constant impedance of the point or line is shown in the diagram below.
Distance Relay Theory
The distance relay is a distance protection device that is used to determine the location of a defective point. The impedance value determines how well this relay works. When the impedance of the defective point is less than the impedance of the relay, it trips the circuit breaker and shuts the connections. The relay continually monitors the voltage and current passing through the PT and CT, and it only operates when the ratio of voltage and current (impedance value) is less than the relay’s specified impedance value.
Types of Distance Relay
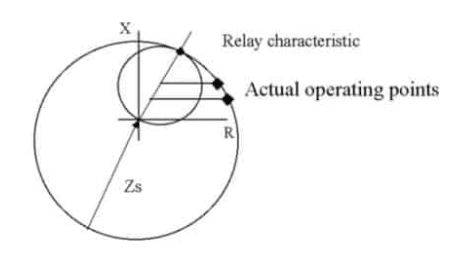
01. Impedance Relay:
The relay estimates impedance up to the point of fault and provides a tripping command if this impedance is less than the relay setting Z. The circular characteristic of the impedance relay is centered at the origin of the R-X diagram. It is mostly utilized as a defect detector and is nondirectional.
02. Admittance Relay:
The most common distance relay is the admittance relay. In pilot schemes, it serves as the tripping_relay, while in step distance schemes, it serves as the backup relay. Its characteristic is directional since it goes through the R-X diagram’s origin. It is round in the electromechanical design and can be curved to conform to the transmission line impedance in the solid-state design.
03. Reactance Relay:
A reactance relay is appropriate for the protection of a short transmission line because its operation is independent of arc resistance. The relay which is designated for a long transmission line should be slightly affected due to power swings.
Working of Distance Relay
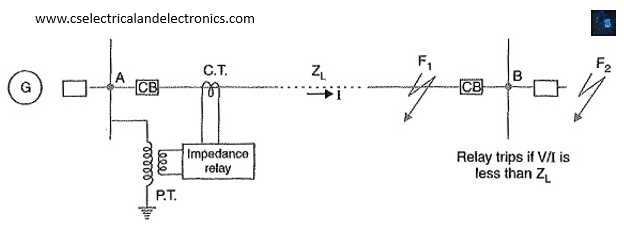
The voltage is computed from the potential transformer, and the current is derived from the current transformer, to determine the impedance. Now, two essential torques play a critical part in the relay’s operation. The one deflects torque, while the other restores torque. The importance of these two torques for relay functioning cannot be overstated.
The deflecting torque is generated by the secondary current of the current transformer, and the restoring torque is provided by the voltage of the potential transformer in a distance_relay. The restoring torque is larger than the deflecting torque under normal operating circumstances.
As a result, the relay stays in a non-operational state. When a fault arises, however, the fault currents rise, increasing the deflecting torque. As a result, the deflecting torque exceeds the restoring torque, and the relay engages. It closed the circuit by moving its dynamic elements whenever the deflecting torque was raised. The travel circuit has been completed.
The circuit breaker is activated after the trip circuit is closed. The circuit tripping might essentially be an electromagnetic switch. When the circuit is turned on, the breaker’s closed contacts open. The problematic line is isolated from the healthy section of the system when the connections are opened. The fault line is isolated in this manner. When the contacts open, an arc forms between them, which must be extinguished.
Advantages of Distance Relay
The advantages of distance relay over overcurrent_relay are given below
- It takes the place of overcurrent transmission line protection.
- Protects promptly.
- It’s really easy to coordinate and apply.
- There is no need to alter the settings because they are permanent.
- The fault current magnitude is reduced as a result of a generation of fault levels.
- Allows for the high-load lining.
Disadvantages of Distance Relay
The disadvantages of distance relay or impedance_relay are shown below
- It is considered to be non-directional since it operates on both sides of a line’s fault.
- It is unable to distinguish between interior and exterior line faults.
- The distance relay’s function is influenced by the resistance of a fault line’s arc. When a defect occurs at any point, an arc is created.
- Because the region covered by the circle on the sides of the R-X plane is vast, power swings have an impact on distance_relay performance.
- Fault resistance measuring capability is restricted.
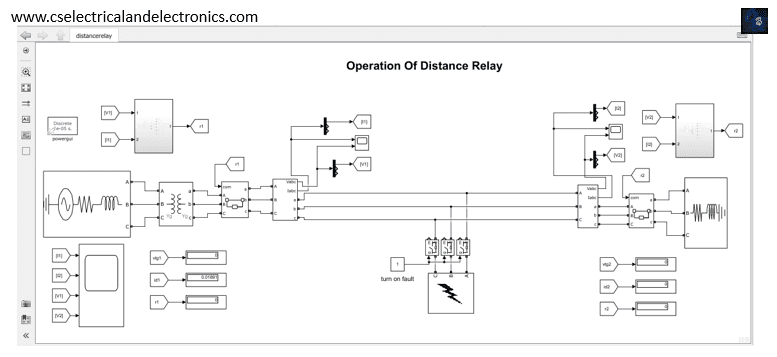
To summarise, distance protection systems are often used to safeguard AC transmission lines and distribution lines from three-phase faults, phase-to-phase faults, and phase-to-ground faults as the primary protection and backup protection.
I hope this article may help you all a lot. Thank you for reading.
Also, read:
- 10 Tips To Maintain Battery For Long Life, Battery Maintainance
- 10 Tips To Save Electricity Bills, Save Money By Saving Electricity
- 100 (AI) Artificial Intelligence Applications In The Automotive Industry
- 100 + Electrical Engineering Projects For Students, Engineers
- 1000+ Control System Quiz, Top MCQ On Control System
- 1000+ Electrical Machines Quiz, Top MCQs On Electrical Machines
- 1000+ MATLAB Simulink Projects For MTech, Engineering Students
- 50 Tips To Save Electricity At Home, Shop, Industry, Office
Author Profile
- Chetu
- Interest's ~ Engineering | Entrepreneurship | Politics | History | Travelling | Content Writing | Technology | Cooking
Latest entries
 All PostsApril 29, 2024Top 11 Free Courses On Battery For Engineers With Documents
All PostsApril 29, 2024Top 11 Free Courses On Battery For Engineers With Documents All PostsApril 19, 2024What Is Vector CANoe Tool, Why It Is Used In The Automotive Industry
All PostsApril 19, 2024What Is Vector CANoe Tool, Why It Is Used In The Automotive Industry All PostsApril 13, 2024What Is TCM, Transmission Control Module, Working, Purpose,
All PostsApril 13, 2024What Is TCM, Transmission Control Module, Working, Purpose, All PostsApril 12, 2024Top 100 HiL hardware in loop Interview Questions With Answers For Engineers
All PostsApril 12, 2024Top 100 HiL hardware in loop Interview Questions With Answers For Engineers