What Is ADC, How Analog To Digital Converters Works, Types Of ADC
Hello guys, welcome back to my blog. In this article, I will discuss what is ADC, how ADC works, how analog to digital converters work, types of analog to digital converters, advantages, disadvantages, and applications of ADC.
If you have any doubts related to electrical, electronics, and computer science, then ask questions. You can also catch me on Instagram – Chetan Shidling.
Also, read:
- What Is Malware, Types Of Malware That Will Kill Your System, Prevention
- Top Applications Of CAN, LIN, Ethernet, FlexRay, USB, & Their Speed
- What Is Marx Generator, Working, Circuit Design, Applications
What Is ADC
Analog to digital converter is popularly known as ADC. ADC is an electronic device that is used to convert the analog signal into a digital signal. The analog signal which consists of the continuous-time and continuous amplitude is given as input to the ADC whereas the output digital signal is of discrete-time and discrete amplitude from the ADC.
In our present world, every real quantity will exist in the analog state. Such analog states cannot be manipulated by any of the digital devices such as mobiles, computers, etc., so to measure the quantity or quality of the analog state quantities by the digital devices we need to convert the analog state to the digital state. So to rectify this problem, the research scientist in IBM named M. Klein invented this ADC in the year 1974. By using ADC we can convert the analog state into the digital state where the digital devices can measure the desired quantities with ease.
Working Of ADC / Analog To Digital Converter
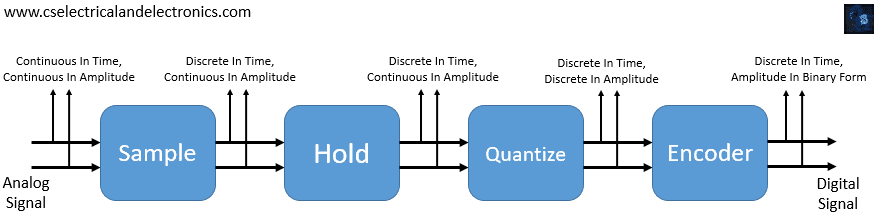
The above block diagram represents the operation and the elements involved in the analog to digital converter. the analog signal is first passed through the sample block which will provide the sample of the signal with the same frequency and that signal is held through the holding block and that sample signal is passed through the quantize block which will provide the discrete value of the amplitude and at last the encoder will convert that discrete amplitude value to the binary code where the digital devices can analyze the signal. Let us deeply discuss the individual blocks of the ADC:
01. Sample
Sample block plays a key role in the conversion of the signal as it is the first block to provide the samples. The sample is provided at the specific time interval which consists of the real value but they are discrete with respect to the time. The sampling frequency is the most important factor which is set according to the requirement of the digital equipment of the system.
02. Hold
The sample block generates the different types of samples so a second block hold is used to hold the sample until the generation of the next sample. Hold has no special function other than holding the present sample until the sample block sends the other sample. This is the main operation of the holding block in the analog to digital converter (ADC).
03. Quantize
The sample on hold will pass through the third block of the converter called Quantize. This quantized block will perform the operation of converting the sampled signal’s continuous value into the digital value which consists of discrete-time and the discrete amplitude. This quantized block will convert the whole continuous signal to the partial digital form.
04. Encoder
The quantized block will provide the sample with the discrete amplitude and the discrete-time. The encoder block input will be the partial digital signal where it will be converted to the full-fledged digital signal by converting it into binary data. Binary data is the language where the digital devices can take them as the input signal.
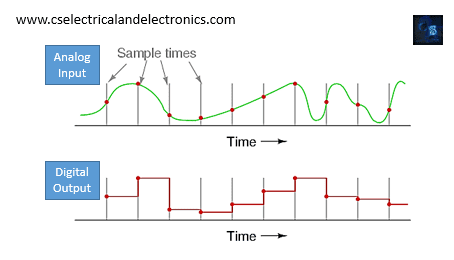
This is how the analog signal is converted into the digital signal using the analog-digital converter- ADC. There are different types of the ADC’s used in the different conversions in the electrical and electronic fields. There are mainly four types of analog to digital converters used in the present world.
Types Of ADC / Analog To Digital Converter
01. FLASH ADC
This flash ADC is also called parallel ADC, which is mostly used ADC because of its speed. This flash analog to digital converter consists of the comparators connected in series which measures and compares the input voltages. It consists of a priority encoder that will provide the required efficient binary data. This ADC is highly expensive and it possesses high-speed working characteristics.
02. PIPELINED ADC
The pipelined ADC consists of the successive approximation quantizers which will look after the samples generated. The input is ready for execution as it is the pipeline technologies advantage. The coarse conversion is the important step in the pipelined ADC.
03. SUCCESSIVE APPROXIMATION ADC
The SAR ADC is the modest technology of the ADC. It uses digital logic which will provide us the closest value of the analog value. The circuit of the SAR ADC mainly consists of the comparators, output latches and the successive approximation register (SAR), and the D/A converter. The SAR is used to clear the MSB value of the input signal if the comparator output is low compared to the value. The SAR plays a key role in the fast and efficient conversion of the analog to the digital state.
04. SIGMA-DELTA ADC
The sigma-delta converters are also called the oversampling converters. It consists of mainly two blocks sigma-delta modulator and the digital filter. The sigma-delta modulator is made up of the integrator and the comparator in addition to single-bit DAC. The digital filter acts as the binary data converter. It consists of the priority encoder which will convert the digital value to the binary data which is taken as input to the digital devices.
The above-mentioned are the most used analog to digital converters in the real world. Now let us go with the advantages and the disadvantages of the Analog to Digital Converter.
Advantages Of ADC / Analog To Digital Converter
- The pipelined analog to digital converters provide the high resolution at high speed.
- Flash A/D are the fastest converters compared to all the converters.
- Successive approximation converters are more reliable and operate as HIGH-speed ADC.
- Sigma-delta A/D converters provide high resolution compared to all the converters.
Disadvantages Of ADC / Analog To Digital Converter
- Flash A/D converters are highly expensive.
- The circuit will become complex as the comparators in the circuit increases.
- The working of the successive approximation ADC will be very slow under high resolution.
- Pipeline A/D converters are very sensitive to the PCB layout.
- The conversion process becomes comparatively difficult in the pipeline ADCs as the non-periodic rate will be comparatively high.
Applications Of ADC / Analog To Digital Converter
- ADCs are used in the Audio and video devices.
- Digital multimeters and Plcs are equipped with the ADCs.
- They are used in the mobile phones.
- They are used for analog medical image processing and also in the medical instrumentation.
- They are used in the oscilloscopes and the RADAR processing.
I hope this article may help you all a lot. Thank you for reading.
Also, read:
- 100 + Electrical Engineering Projects For Students, Engineers
- 1000+ Electronics Projects For Engineers, Diploma, MTech Students
- 1000+ MATLAB Simulink Projects For MTech, Engineering Students
- 500+ Embedded System Projects For Engineer, Diploma, MTech, PhD
- 500+ Projects For Diploma Electrical, Electronics Student, Diploma Project
- 8051 Microcontroller Timers, TCON Register, TMOD Register
- Advancements In 3D Printing Technology And It’s Future
- Advancements In Power Electronics For Energy Efficiency
Author Profile
- Chetu
- Interest's ~ Engineering | Entrepreneurship | Politics | History | Travelling | Content Writing | Technology | Cooking
Latest entries
 All PostsApril 29, 2024Top 11 Free Courses On Battery For Engineers With Documents
All PostsApril 29, 2024Top 11 Free Courses On Battery For Engineers With Documents All PostsApril 19, 2024What Is Vector CANoe Tool, Why It Is Used In The Automotive Industry
All PostsApril 19, 2024What Is Vector CANoe Tool, Why It Is Used In The Automotive Industry All PostsApril 13, 2024What Is TCM, Transmission Control Module, Working, Purpose,
All PostsApril 13, 2024What Is TCM, Transmission Control Module, Working, Purpose, All PostsApril 12, 2024Top 100 HiL hardware in loop Interview Questions With Answers For Engineers
All PostsApril 12, 2024Top 100 HiL hardware in loop Interview Questions With Answers For Engineers